-
We've released a release candidate of the next major version of Wrangler, the CLI for Cloudflare Workers —
wrangler@4.0.0-rc.0.You can run the following command to install it and be one of the first to try it out:
Terminal window npm i wrangler@v4-rcTerminal window pnpm add wrangler@v4-rcTerminal window yarn add wrangler@v4-rcUnlike previous major versions of Wrangler, which were foundational rewrites ↗ and rearchitectures ↗ — Version 4 of Wrangler includes a much smaller set of changes. If you use Wrangler today, your workflow is very unlikely to change. Before we release Wrangler v4 and advance past the release candidate stage, we'll share a detailed migration guide in the Workers developer docs. But for the vast majority of cases, you won't need to do anything to migrate — things will just work as they do today. We are sharing this release candidate in advance of the official release of v4, so that you can try it out early and share feedback.
Version 4 of Wrangler updates the version of esbuild ↗ that Wrangler uses internally, allowing you to use modern JavaScript language features, including:
The
usingkeyword from the Explicit Resource Management standard makes it easier to work with the JavaScript-native RPC system built into Workers. This means that when you obtain a stub, you can ensure that it is automatically disposed when you exit scope it was created in:function sendEmail(id, message) {using user = await env.USER_SERVICE.findUser(id);await user.sendEmail(message);// user[Symbol.dispose]() is implicitly called at the end of the scope.}Import attributes ↗ allow you to denote the type or other attributes of the module that your code imports. For example, you can import a JSON module, using the following syntax:
import data from "./data.json" with { type: "json" };All commands that access resources (for example,
wrangler kv,wrangler r2,wrangler d1) now access local datastores by default, ensuring consistent behavior.Moving forward, the active, maintenance, and current versions of Node.js ↗ will be officially supported by Wrangler. This means the minimum officially supported version of Node.js you must have installed for Wrangler v4 will be Node.js v18 or later. This policy mirrors how many other packages and CLIs support older versions of Node.js, and ensures that as long as you are using a version of Node.js that the Node.js project itself supports, this will be supported by Wrangler as well.
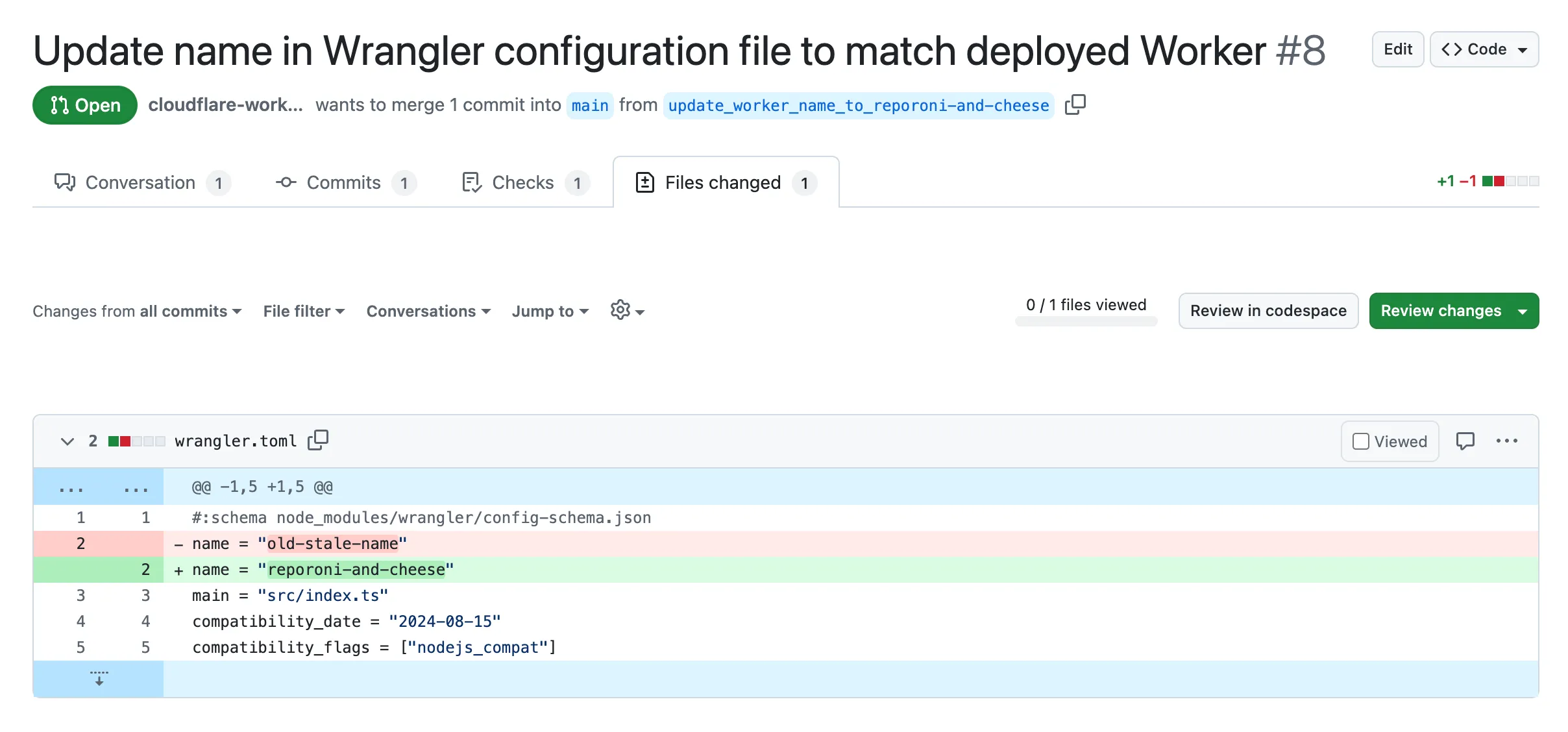
All previously deprecated features in Wrangler v2 ↗ and in Wrangler v3 ↗ have now been removed. Additionally, the following features that were deprecated during the Wrangler v3 release have been removed:
- Legacy Assets (using
wrangler dev/deploy --legacy-assetsor thelegacy_assetsconfig file property). Instead, we recommend you migrate to Workers assets ↗. - Legacy Node.js compatibility (using
wrangler dev/deploy --node-compator thenode_compatconfig file property). Instead, use thenodejs_compatcompatibility flag ↗. This includes the functionality from legacynode_compatpolyfills and natively implemented Node.js APIs. wrangler version. Instead, usewrangler --versionto check the current version of Wrangler.getBindingsProxy()(viaimport { getBindingsProxy } from "wrangler"). Instead, use thegetPlatformProxy()API ↗, which takes exactly the same arguments.usage_model. This no longer has any effect, after the rollout of Workers Standard Pricing ↗.
We'd love your feedback! If you find a bug or hit a roadblock when upgrading to Wrangler v4, open an issue on the
cloudflare/workers-sdkrepository on GitHub ↗. - Legacy Assets (using
-
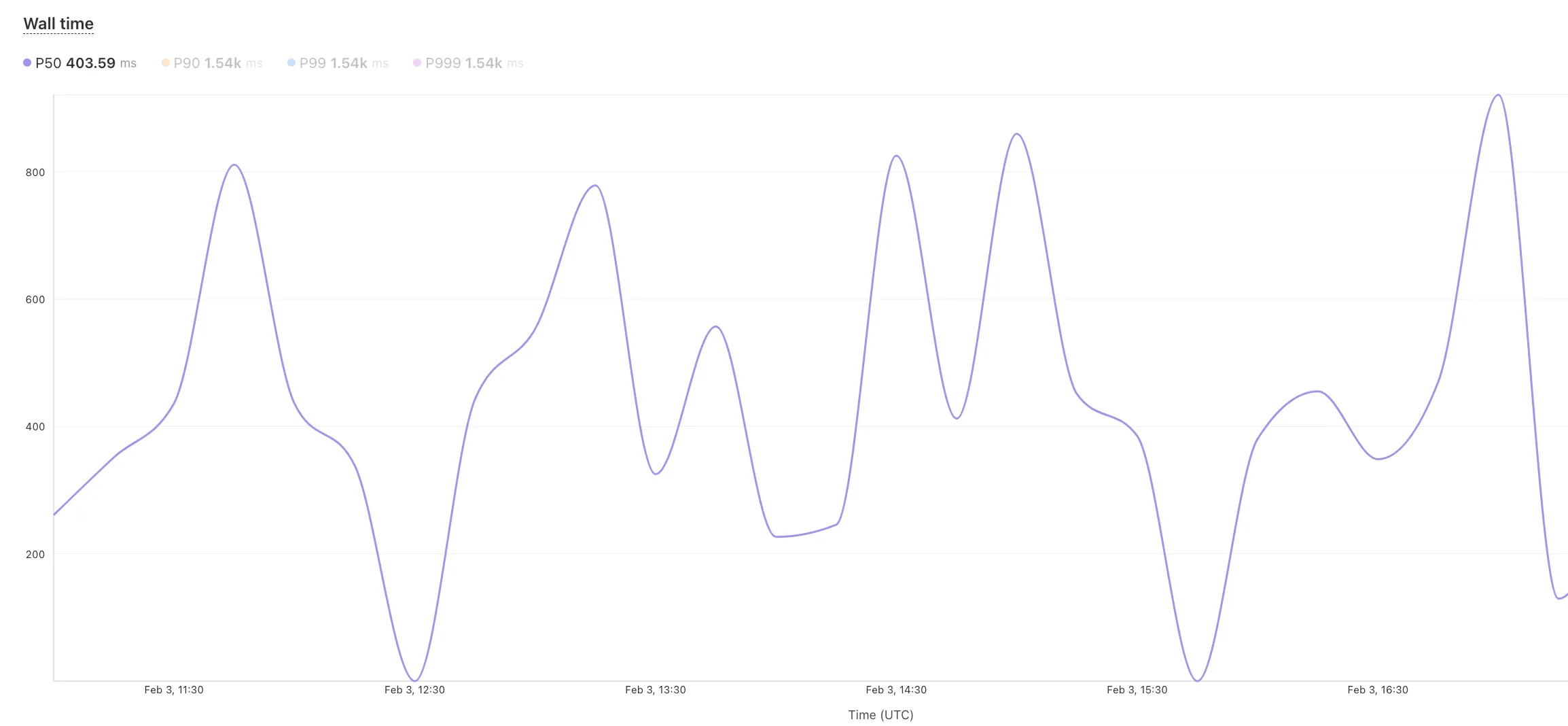
Radar has expanded its DNS insights, providing visibility into aggregated traffic and usage trends observed by our 1.1.1.1 DNS resolver. In addition to global, location, and ASN traffic trends, we are also providing perspectives on protocol usage, query/response characteristics, and DNSSEC usage.
Previously limited to the
toplocations and ASes endpoints, we have now introduced the following endpoints:timeseries: Retrieves DNS query volume over time.summary: Retrieves summaries of DNS query distribution across ten different dimensions.timeseries_group: Retrieves timeseries data for DNS query distribution across ten different dimensions.
For the
summaryandtimeseries_groupsendpoints, the following dimensions are available, displaying the distribution of DNS queries based on:cache_hit: Cache status (hit vs. miss).dnsssec: DNSSEC support status (secure, insecure, invalid or other).dnsssec_aware: DNSSEC client awareness (aware vs. not-aware).dnsssec_e2e: End-to-end security (secure vs. insecure).ip_version: IP version (IPv4 vs. IPv6).matching_answer: Matching answer status (match vs. no-match).protocol: Transport protocol (UDP, TLS, HTTPS or TCP).query_type: Query type (A,AAAA,PTR, etc.).response_code: Response code (NOERROR,NXDOMAIN,REFUSED, etc.).response_ttl: Response TTL.
Learn more about the new Radar DNS insights in our blog post ↗, and check out the new Radar page ↗.
-
We've released a new REST API for Browser Rendering in open beta, making interacting with browsers easier than ever. This new API provides endpoints for common browser actions, with more to be added in the future.
With the REST API you can:
- Capture screenshots – Use
/screenshotto take a screenshot of a webpage from provided URL or HTML. - Generate PDFs – Use
/pdfto convert web pages into PDFs. - Extract HTML content – Use
/contentto retrieve the full HTML from a page. Snapshot (HTML + Screenshot) – Use/snapshotto capture both the page's HTML and a screenshot in one request - Scrape Web Elements – Use
/scrapeto extract specific elements from a page.
For example, to capture a screenshot:
Screenshot example curl -X POST 'https://api.cloudflare.com/client/v4/accounts/<accountId>/browser-rendering/screenshot' \-H 'Authorization: Bearer <apiToken>' \-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \-d '{"html": "Hello World!","screenshotOptions": {"type": "webp","omitBackground": true}}' \--output "screenshot.webp"Learn more in our documentation.
- Capture screenshots – Use
-
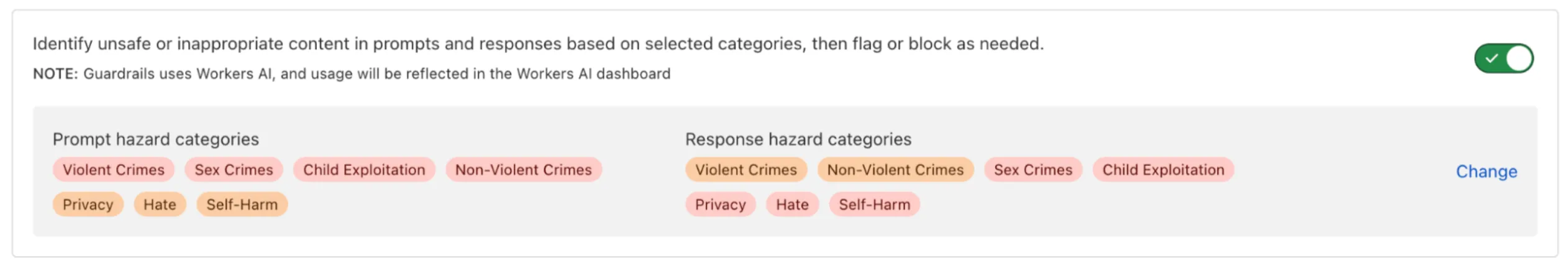
AI Gateway now includes Guardrails, to help you monitor your AI apps for harmful or inappropriate content and deploy safely.
Within the AI Gateway settings, you can configure:
- Guardrails: Enable or disable content moderation as needed.
- Evaluation scope: Select whether to moderate user prompts, model responses, or both.
- Hazard categories: Specify which categories to monitor and determine whether detected inappropriate content should be blocked or flagged.
Learn more in the blog ↗ or our documentation.
-
Workers AI now supports structured JSON outputs with JSON mode, which allows you to request a structured output response when interacting with AI models.
This makes it much easier to retrieve structured data from your AI models, and avoids the (error prone!) need to parse large unstructured text responses to extract your data.
JSON mode in Workers AI is compatible with the OpenAI SDK's structured outputs ↗
response_formatAPI, which can be used directly in a Worker:import { OpenAI } from "openai";// Define your JSON schema for a calendar eventconst CalendarEventSchema = {type: "object",properties: {name: { type: "string" },date: { type: "string" },participants: { type: "array", items: { type: "string" } },},required: ["name", "date", "participants"],};export default {async fetch(request, env) {const client = new OpenAI({apiKey: env.OPENAI_API_KEY,// Optional: use AI Gateway to bring logs, evals & caching to your AI requests// https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/providers/openai/// baseUrl: "https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai"});const response = await client.chat.completions.create({model: "gpt-4o-2024-08-06",messages: [{ role: "system", content: "Extract the event information." },{role: "user",content: "Alice and Bob are going to a science fair on Friday.",},],// Use the `response_format` option to request a structured JSON outputresponse_format: {// Set json_schema and provide ra schema, or json_object and parse it yourselftype: "json_schema",schema: CalendarEventSchema, // provide a schema},});// This will be of type CalendarEventSchemaconst event = response.choices[0].message.parsed;return Response.json({calendar_event: event,});},};import { OpenAI } from "openai";interface Env {OPENAI_API_KEY: string;}// Define your JSON schema for a calendar eventconst CalendarEventSchema = {type: 'object',properties: {name: { type: 'string' },date: { type: 'string' },participants: { type: 'array', items: { type: 'string' } },},required: ['name', 'date', 'participants']};export default {async fetch(request: Request, env: Env) {const client = new OpenAI({apiKey: env.OPENAI_API_KEY,// Optional: use AI Gateway to bring logs, evals & caching to your AI requests// https://developers.cloudflare.com/ai-gateway/providers/openai/// baseUrl: "https://gateway.ai.cloudflare.com/v1/{account_id}/{gateway_id}/openai"});const response = await client.chat.completions.create({model: 'gpt-4o-2024-08-06',messages: [{ role: 'system', content: 'Extract the event information.' },{ role: 'user', content: 'Alice and Bob are going to a science fair on Friday.' },],// Use the `response_format` option to request a structured JSON outputresponse_format: {// Set json_schema and provide ra schema, or json_object and parse it yourselftype: 'json_schema',schema: CalendarEventSchema, // provide a schema},});// This will be of type CalendarEventSchemaconst event = response.choices[0].message.parsed;return Response.json({"calendar_event": event,})}}To learn more about JSON mode and structured outputs, visit the Workers AI documentation.
-
Workflows now supports up to 4,500 concurrent (running) instances, up from the previous limit of 100. This limit will continue to increase during the Workflows open beta. This increase applies to all users on the Workers Paid plan, and takes effect immediately.
Review the Workflows limits documentation and/or dive into the get started guide to start building on Workflows.
-
We've released the agents-sdk ↗, a package and set of tools that help you build and ship AI Agents.
You can get up and running with a chat-based AI Agent ↗ (and deploy it to Workers) that uses the
agents-sdk, tool calling, and state syncing with a React-based front-end by running the following command:Terminal window npm create cloudflare@latest agents-starter -- --template="cloudflare/agents-starter"# open up README.md and follow the instructionsYou can also add an Agent to any existing Workers application by installing the
agents-sdkpackage directlyTerminal window npm i agents-sdk... and then define your first Agent:
import { Agent } from 'agents-sdk';export class YourAgent extends Agent<Env> {// Build it out// Access state on this.state or query the Agent's database via this.sql// Handle WebSocket events with onConnect and onMessage// Run tasks on a schedule with this.schedule// Call AI models// ... and/or call other Agents.}Head over to the Agents documentation to learn more about the
agents-sdk, the SDK APIs, as well as how to test and deploying agents to production.
-
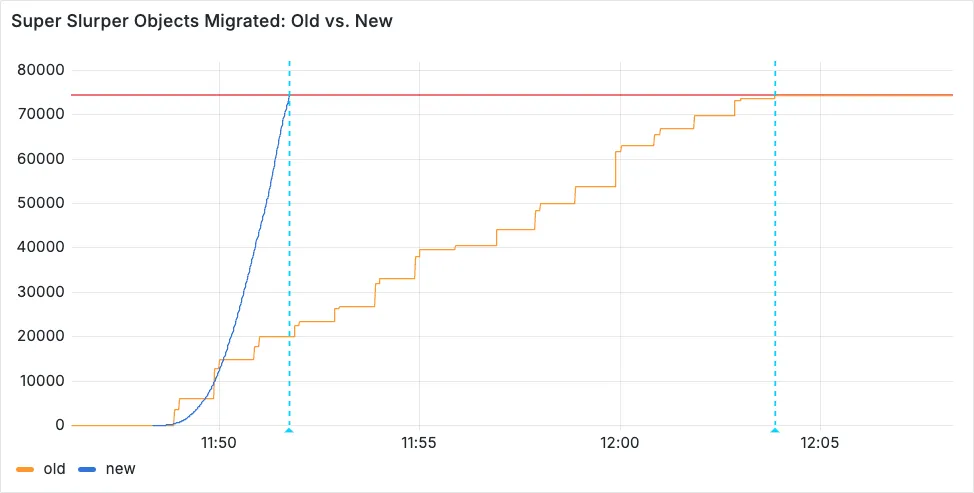
Super Slurper can now migrate data from any S3-compatible object storage provider to Cloudflare R2. This includes transfers from services like MinIO, Wasabi, Backblaze B2, and DigitalOcean Spaces.
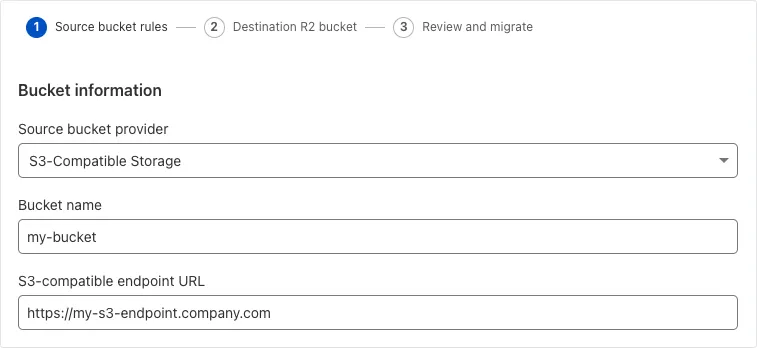
For more information on Super Slurper and how to migrate data from your existing S3-compatible storage buckets to R2, refer to our documentation.
-
You can now interact with the Images API directly in your Worker.
This allows more fine-grained control over transformation request flows and cache behavior. For example, you can resize, manipulate, and overlay images without requiring them to be accessible through a URL.
The Images binding can be configured in the Cloudflare dashboard for your Worker or in the
wrangler.tomlfile in your project's directory:[images]binding = "IMAGES" # i.e. available in your Worker on env.IMAGESWithin your Worker code, you can interact with this binding by using
env.IMAGES.Here's how you can rotate, resize, and blur an image, then output the image as AVIF:
const info = await env.IMAGES.info(stream);// stream contains a valid image, and width/height is available on the info objectconst response = (await env.IMAGES.input(stream).transform({ rotate: 90 }).transform({ width: 128 }).output({ format: "image/avif" })).response();return response;For more information, refer to Images Bindings.
-
We've updated the Workers AI text generation models to include context windows and limits definitions and changed our APIs to estimate and validate the number of tokens in the input prompt, not the number of characters.
This update allows developers to use larger context windows when interacting with Workers AI models, which can lead to better and more accurate results.
Our catalog page provides more information about each model's supported context window.